Social and Financial Impact of Virtual Public Transport: Self-Reliance, Care and Work

Social and Financial Impact of Virtual Public Transport: Self-Reliance, Care and Work
Social and Financial Impact of Virtual Public Transport: Self-Reliance, Care and Work
The pressure on care and transportation services for people with disabilities or vulnerabilities in the Netherlands has been steadily increasing for years. Municipalities and healthcare organizations face challenges due to an aging population, growing and more complex care demands, and ever-increasing mobility needs. At the same time, societal demands for greater independence, participation, and inclusion are growing – because everyone deserves an equal opportunity to participate.
Rising Costs and Pressure on Facilities
The costs of student transport and targeted group transport are substantial and increase by approximately five percent annually. In 2021/2022, for example, over 72,000 students used municipal student transport, with a total cost of €236 million. Social Support Act (Wmo) transport also has a large number of users: 340,000–380,000, representing a total annual cost of €600–680 million. Municipalities are struggling with budget overruns and are seeking more efficient, sustainable solutions.
The Importance of Self-Reliance
The call for solutions that enable people with disabilities to function independently is becoming increasingly urgent. Self-reliance literally opens doors to employment, education, and a more independent life – resulting in greater social participation and economic value. At the same time, increasing independence has a direct impact on well-being and reduces the need for care and support.
Economic Impact of Participation
independently brings people closer to work and education. The economic value per participant is estimated to be between €20,000 and €25,000 per year. If just 10,000 more people could participate in the labor market, this would generate at least €200–250 million annually. International research confirms that digital support (such as VR training) not only increases labor participation but also reduces support costs.
Healthcare savings through smart technology
The annual healthcare costs for people with intellectual disabilities or autism are high: €30,000–40,000 and €10,000–20,000 per person per year, respectively. Modern technology can offer a solution. In practice, VR training has been shown to reduce healthcare demand by 5–10%, with structural savings of up to €105 million per year for some of the target group. Moreover, they reduce the influx into sheltered housing and mental healthcare by improving independence and mental resilience.
The Social and Financial Potential
If 20% of target group transport users switch to regular public transport using VR exercises, this represents a direct annual savings of €266 million in transport costs. Add to that increased labor participation and reduced demand for healthcare: the total social and economic potential amounts to hundreds of millions of euros per year.
Innovation: The power of Virtual Public Transport
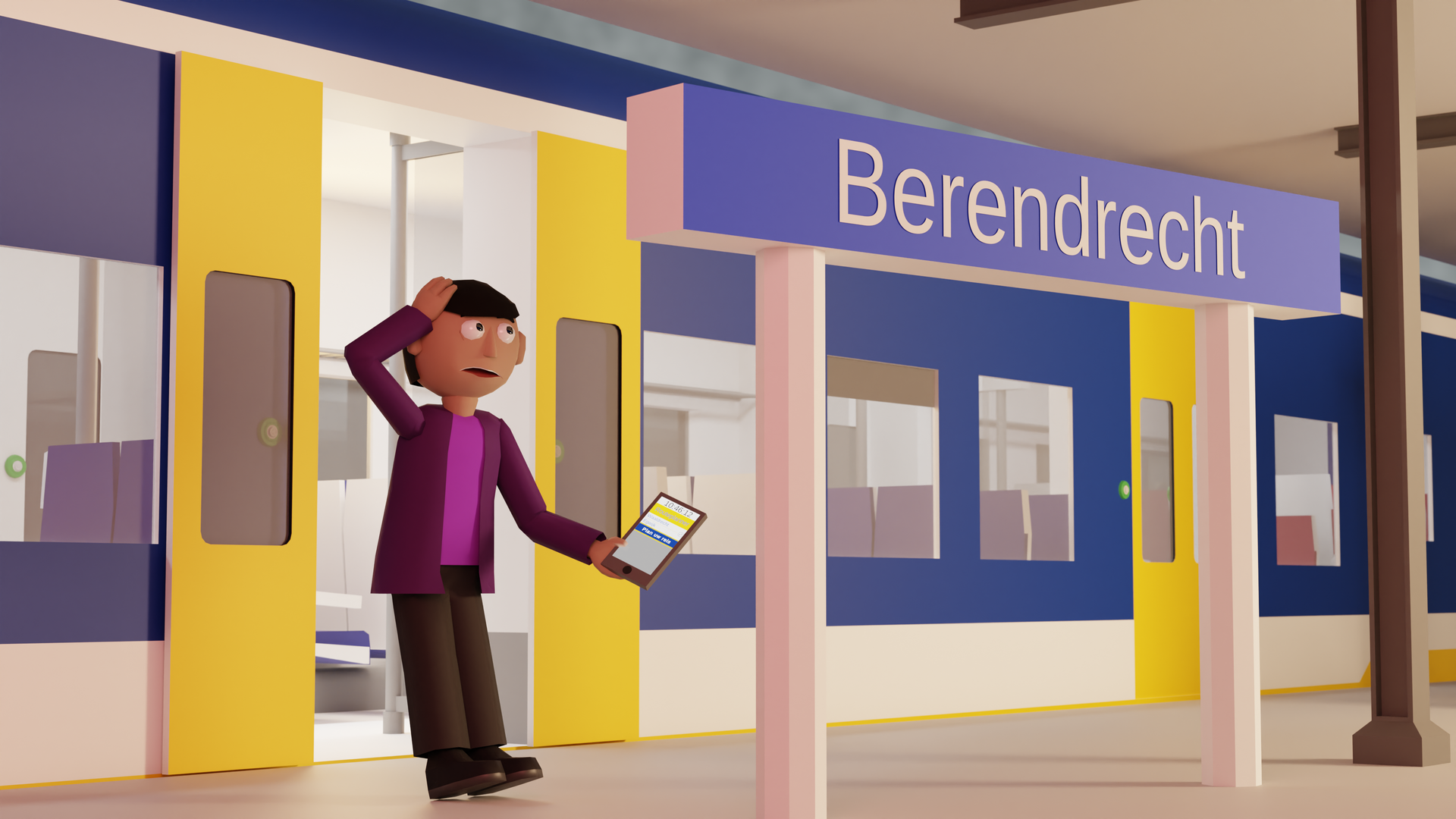
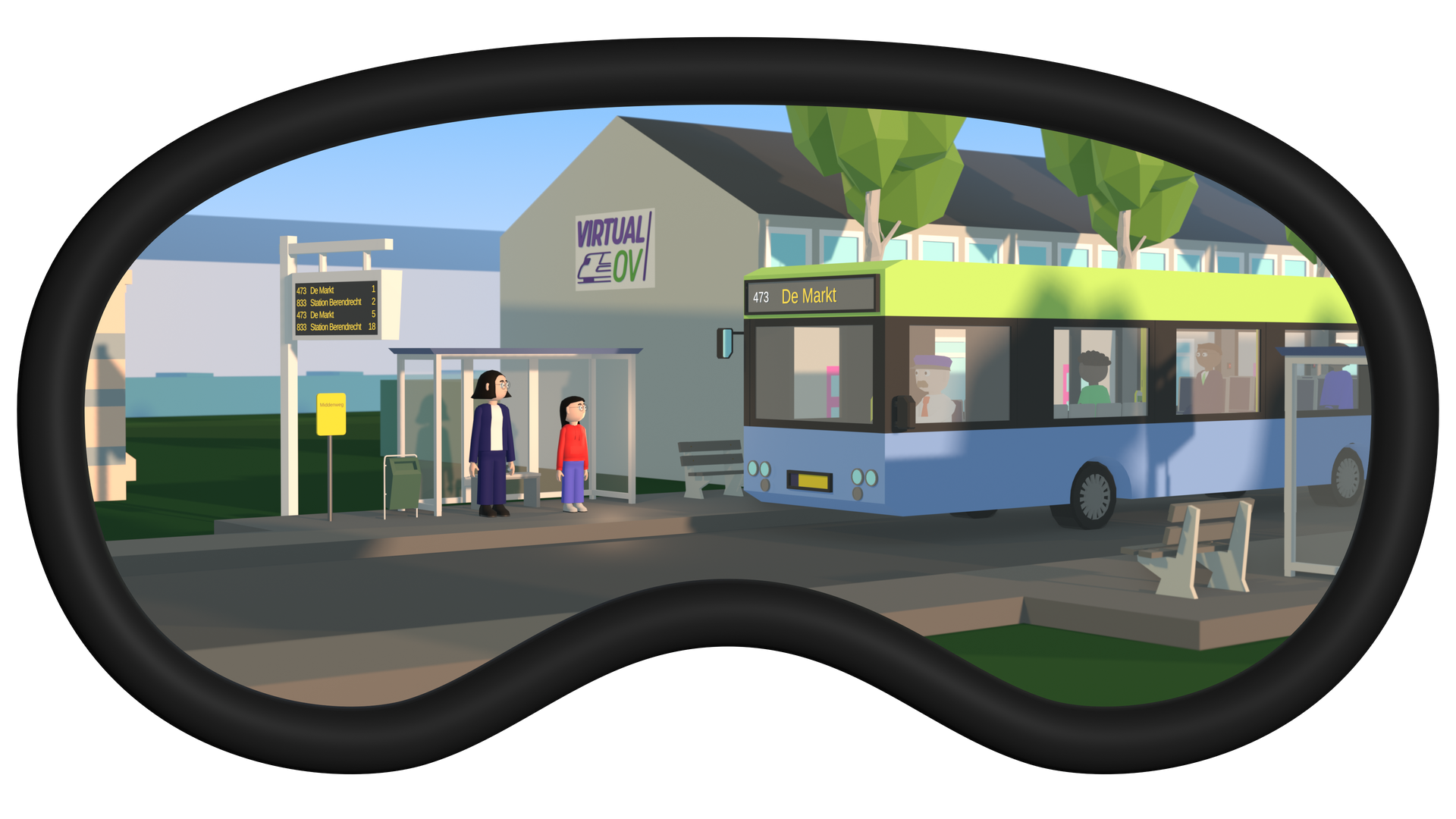
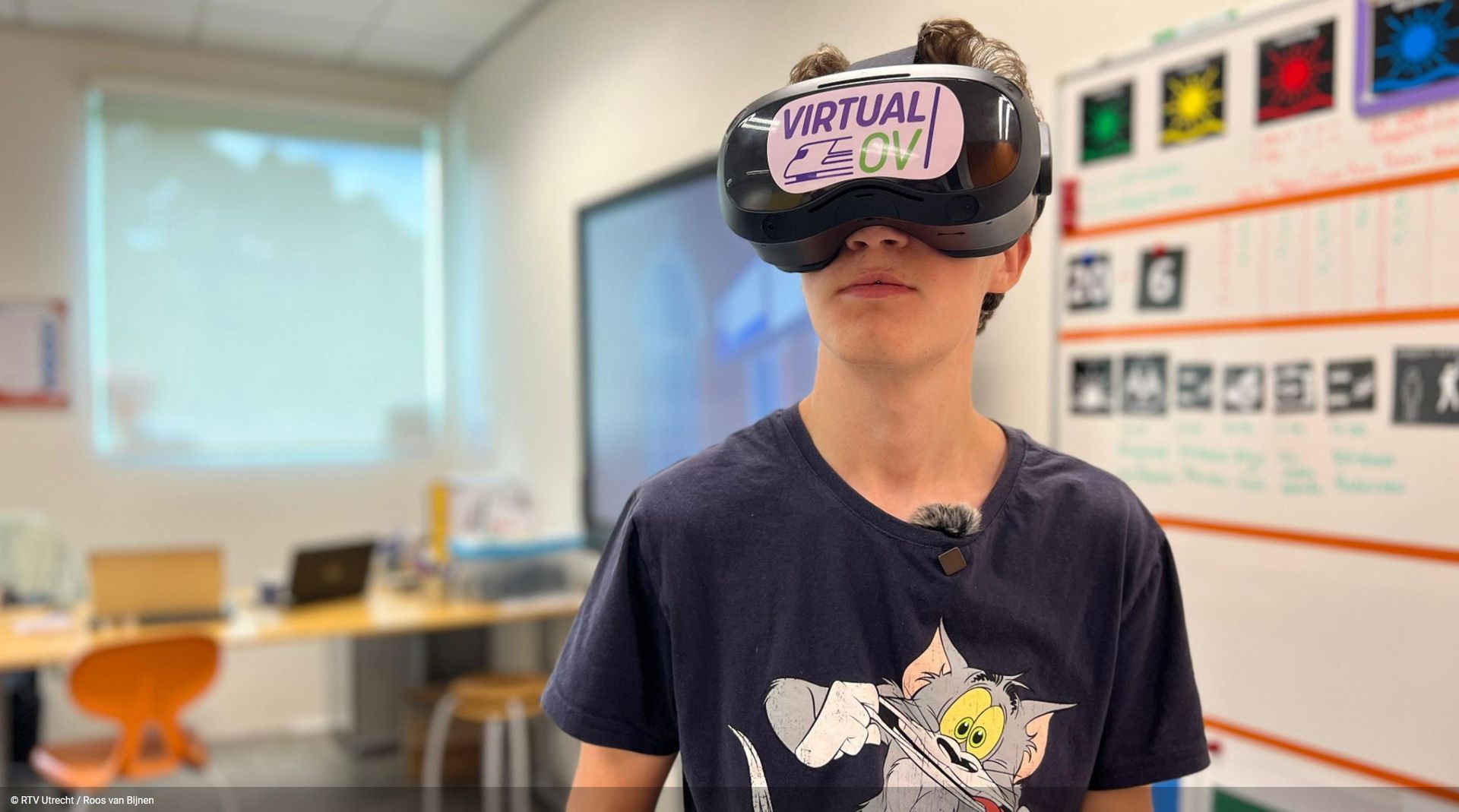
Virtual OV offers neurodivergent individuals a safe, realistic learning environment to learn to travel independently on public transport. They practice realistic scenarios, develop executive functions, and gain experience – making the step to self-reliance easier and more sustainable. The platform promotes inclusion, mobility, and personal growth through personalized guidance and continuous monitoring of the learning process.
Conclusion
Healthcare and transportation costs are rising, challenges are becoming more complex, and societal demands for inclusion and independence are growing louder. By deploying smart technology, such as Virtual Public Transport, it's possible to address these problems structurally. The result? More people who can participate independently in society, substantially lower costs, and a powerful social impact. Virtual Public Transport is therefore much more than a technological innovation: it's a strategic solution for sustainable change.